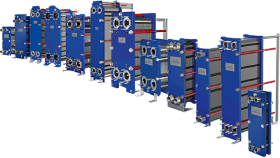
A gasketed plate heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between two fluids. These devices are commonly used in industries that require efficient heating or cooling processes. A gasketed plate heat exchanger consists of several thin metal plates stacked together. Gaskets are placed between these plates to keep the fluids separate and control their flow. This design is simple yet highly effective, making it popular for a wide range of applications.
In this blog, we’ll explore how gasketed plate heat exchangers work, what materials they are made of, and where they are commonly used.
Understanding the Working Principle of a Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger
A gasketed plate heat exchanger works by channelling two fluids through separate pathways. In this way, heat can pass from one fluid to another without mixing them. The metal plates create a large surface area for heat transfer.
As the hot fluid flows on one side of each plate and the cool fluid flows on the opposite side, heat transfers across the plate surface. The fluids never come into direct contact, because of the gaskets.
These gaskets, typically made from rubber or similar flexible materials, act as seals between the plates. They prevent leakage and direct the fluid flow in a specific pattern. This flow pattern often takes a zig-zag path, increasing contact time and improving heat transfer efficiency.
The plates themselves are typically corrugated to maximize surface area and increase the turbulence of the fluids. This helps improve the rate of heat transfer by keeping the fluids mixed as they flow.
Materials Used in Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are usually made from durable metals that conduct heat well and resist corrosion. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, and other alloys. The choice of material depends on the fluids used and the operating conditions, such as temperature and pressure.
Stainless steel is popular because it is strong, corrosion-resistant, and works well with many fluids. However, for more aggressive chemicals or higher temperatures, materials like titanium are preferred.
The gaskets are often made of rubber or other elastomers that can handle different chemicals and temperatures. Different types of gaskets are selected based on the type of fluid used, as well as the heat exchanger’s operating temperature and pressure.
Key Applications of Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
HVAC Systems
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are commonly used in HVAC systems to efficiently transfer heat between heating and cooling systems. This helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing energy costs.
Refrigeration
These plate heat exchangers play a crucial role in refrigeration by cooling and condensing refrigerants used in various cooling processes. They support precise and efficient temperature control, which is essential for refrigeration systems.
Food and Beverage Industry
In this industry, gasketed plate heat exchangers are widely used to pasteurize and cool liquids such as milk, juice, and beer. Their design ensures product safety and quality by preventing contamination during the heat exchange process.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, these heat exchangers help control reaction temperatures by transferring heat between different chemical fluids. This precise temperature control is essential for safe and efficient chemical reactions.
Pharmaceutical Industry
These heat exchangers are essential in the pharmaceutical industry to maintain strict temperature control during medicine production. They also help ensure sterile conditions in processing environments, which is critical for product safety and quality.
Benefits of Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
High Efficiency
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are highly efficient due to the large surface area of their plates, which allows rapid heat transfer. This efficiency leads to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. Thus making them a cost-effective choice for many industries.
Easy Maintenance
These types of plate heat exchangers are designed for easy maintenance because the plates can be separated. This feature allows thorough cleaning and convenient inspection. This is especially valuable in industries that require frequent sanitation, such as food production and pharmaceuticals.
Flexible Design
The modular design of these heat exchangers allows operators to easily add or remove plates. This adaptability makes it easy to adjust the heat exchanger’s capacity, enabling it to meet changing production demands.
Compact and Space-Saving
Due to their plate design, these heat exchangers are compact and take up less floor space compared to bulkier alternatives. This compactness is beneficial for facilities where space is limited.
Reduced Risk of Cross-Contamination
Gaskets in these heat exchangers create a barrier that prevents fluids from mixing, ensuring product purity and safety. This feature is crucial for industries like food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness is a top priority.
Conclusion
In summary, a gasketed plate heat exchanger is an efficient, flexible, and reliable device for transferring heat between two fluids. Its design, consisting of metal plates and gaskets, allows for efficient heat transfer while keeping the fluids separate. These heat exchangers are made from materials like stainless steel and titanium, which help them withstand different operating conditions.
With applications across various industries—such as HVAC, food processing, and chemical processing—gasketed plate heat exchangers are a popular choice for safe, effective heating and cooling. Whether it’s maintaining product purity or maximizing energy efficiency, these devices offer versatile solutions that meet a wide range of industrial needs.